What is GRIHA?
GRIHA is India’s National Rating System for Green buildings. It has been developed by TERI (The Energy and Resources Institute) and is endorsed by the MNRE (Ministry of New and Renewable Energy). It is based on nationally accepted energy and environmental principles, and seeks to strike a balance between established practices and emerging concepts, both national and international.
Five ‘R’ philosophy of sustainable development, namely
- Refuse – to blindly adopt international trends, materials, technologies, products, etc. Specially in areas where local substitutes/equivalents are available
- Reduce – the dependence on high energy products, systems, processes, etc.
- Reuse – materials, products, traditional technologies, so as to reduce the costs incurred in designing buildings as well as in operating them
- Recycle – all possible wastes generated from the building site, during construction, operation and demolition
- Reinvent – engineering systems, designs, and practices such that India creates global examples that the world can follow rather than us following international examples
GRIHA attempts to quantify aspects, such as:
- Energy/ power consumption (in terms of electricity consumed in kWh per square meter per year)
- Water consumption (in terms of litres per person per day)
- Waste generation (in terms of kilograms per day, or litres per day)
- Renewable energy integration (in terms of kW of connected load)
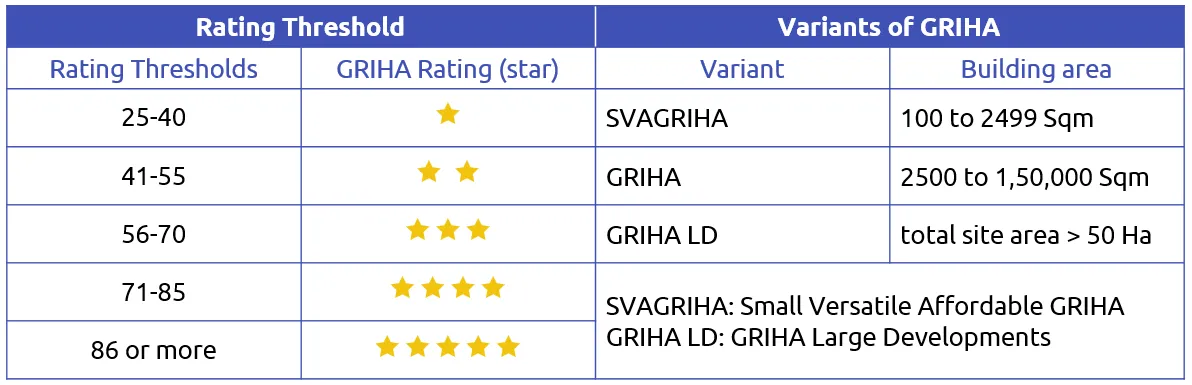
GRIHA Rating and variants: [1]
Some GRIHA registered/rated buildings are Common Wealth Games Village, New Delhi, Suzlon One Earth, Pune – Global headquarters of Suzlon Group, Centre for Environmental Science and Engineering building (CESE) at IIT, Kanpur, etc.
Calculation of Carbon reduction potential
Let’s say, we have a residential complex with plinth area of 10,000 Sqm
As per GRIHA ‐ 70 kWh/Sqm/yr is considered as the benchmark for Residential structure & 90 kWh/Sqm/yr for Non‐residential structure.
For residential building, taking benchmark @ 70 kWh/Sqm/yr.
Hence, benchmark = 70 * 10000 = 700000 kWh/yr.
As per the minimum requirement of GRIHA ‐ 10% savings is considered over the benchmark.
Hence, saving@10% = 700000*10% = 7000 kWh/yr.
Weighted average emission factor = 0.92 kg CO2 per KWh (combined margin) [2]
Carbon reduction potential = 0.92 * 7000 = 64400 kg CO2/yr
Weighted average emission factor = 0.92 kg CO2 per KWh (combined margin) as per CO2 emission factor database, version 15, CEA (Government of India). [2]
Carbon reduction potential = 0.92 * 7000 = 64400 kg CO2/yr
Hence, Carbon reduction potential of the residential building is 64.4 tonne per year of CO2 equivalent.
